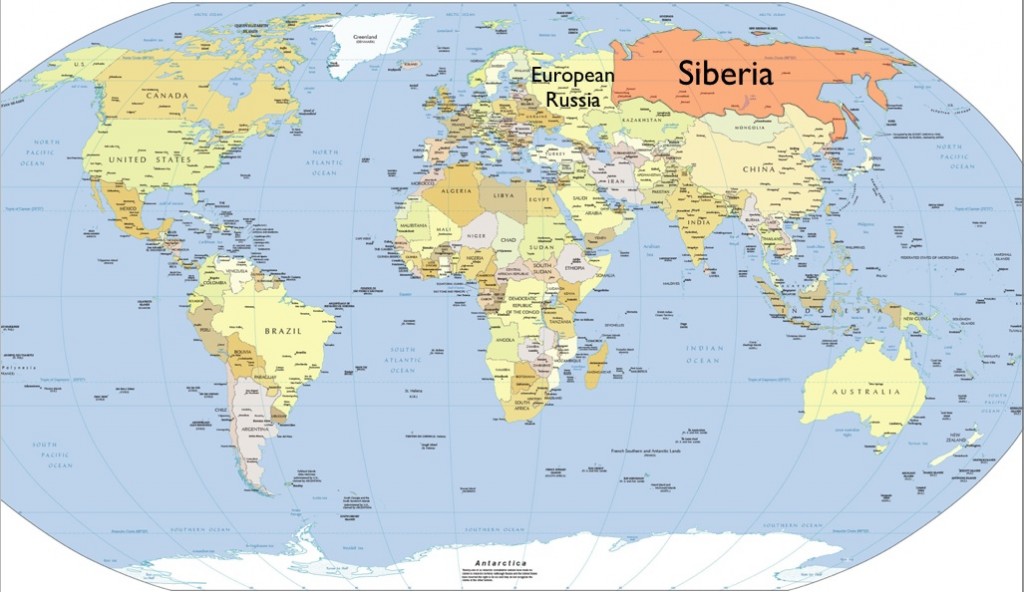
Siberia, a vast and enigmatic region, has long fascinated people around the world. Known for its immense size and challenging climate, Siberia plays a crucial role in global geopolitics, economics, and environmental studies. If you're wondering where is Siberia located, this article will provide you with a detailed overview of its geography, history, and significance.
Siberia stretches across a significant portion of Northern Asia, covering an area larger than many continents. Its vast expanse encompasses diverse landscapes, from frozen tundras to dense forests and majestic mountains. This region's location makes it a critical player in global discussions about climate change, natural resources, and cultural diversity.
In this article, we will delve into the geographical positioning of Siberia, explore its unique features, and highlight its importance in various fields. Whether you're a geography enthusiast, a researcher, or simply curious about this fascinating region, you'll find valuable insights here. Let's begin our journey to discover where Siberia is located and what makes it such a remarkable place.
Read also:Bubbles Tpb Glasses A Comprehensive Guide To Fashion And Functionality
Table of Contents
- Where is Siberia Located?
- Geography of Siberia
- Climate in Siberia
- Natural Resources in Siberia
- Population and Demographics
- Historical Overview of Siberia
- Siberia's Economy
- Environmental Challenges in Siberia
- Tourism in Siberia
- Conclusion
- Sub-Heading: Understanding Siberia's Microclimates
- Sub-Heading: Key Natural Resources
- Sub-Heading: Ethnic Diversity in Siberia
- Sub-Heading: Major Historical Events
- Sub-Heading: Key Economic Sectors
- Sub-Heading: Popular Tourist Destinations
Where is Siberia Located?
Siberia is located in Northern Asia, forming a significant part of the Russian Federation. It spans from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. The region covers approximately 13.1 million square kilometers, making it one of the largest land areas in the world. Siberia's strategic location places it between Europe and the Far East, bridging two major continents.
Geographically, Siberia is bordered by several significant landmarks. To the north, it stretches along the Arctic Ocean, while the south touches the borders of Kazakhstan, Mongolia, and China. The vast expanse of this region includes diverse terrains, from frozen tundras to fertile plains, contributing to its unique identity.
Geography of Siberia
The geography of Siberia is as diverse as it is expansive. The region can be divided into several distinct zones based on its topography and climate. From the icy tundras of the north to the dense taiga forests in the central region, Siberia offers a wide range of landscapes.
Understanding Siberia's Microclimates
Despite its reputation for harsh winters, Siberia exhibits various microclimates depending on the location. Coastal areas near the Pacific Ocean experience milder winters compared to the interior regions. The central and northern parts, however, are known for their extreme cold, with temperatures dropping below -50°C during winter months.
Climate in Siberia
Siberia's climate is predominantly subarctic, characterized by long, cold winters and short, mild summers. The region experiences significant temperature variations, with some areas recording extreme lows and highs. This climate has a profound impact on the region's flora, fauna, and human habitation.
- Winter temperatures can drop below -60°C in some areas.
- Summer temperatures can reach up to 30°C in the southern regions.
- Precipitation levels vary, with higher rainfall in the taiga forests compared to the tundra regions.
Natural Resources in Siberia
Siberia is rich in natural resources, making it a vital region for global trade and industry. The region is home to vast reserves of oil, natural gas, coal, and precious metals. These resources contribute significantly to Russia's economy and global energy markets.
Read also:Mariana Vicente A Rising Star In The Entertainment Industry
Key Natural Resources
Some of the key natural resources found in Siberia include:
- Oil: Siberia holds some of the largest oil reserves in the world.
- Natural Gas: The region is a major supplier of natural gas to Europe and Asia.
- Coal: Extensive coal deposits are found in the Kuznetsk Basin.
- Precious Metals: Gold, platinum, and diamonds are mined in various parts of Siberia.
Population and Demographics
Despite its vast size, Siberia has a relatively low population density. Most of the population resides in urban centers such as Novosibirsk, Omsk, and Krasnoyarsk. The region's population is ethnically diverse, comprising Russians, indigenous peoples, and other minority groups.
Ethnic Diversity in Siberia
Siberia is home to over 40 indigenous ethnic groups, each with its own unique culture and traditions. These groups include the Yakuts, Evenks, and Buryats, among others. The interaction between indigenous cultures and Russian settlers has shaped the region's social fabric over the centuries.
Historical Overview of Siberia
The history of Siberia dates back thousands of years, with evidence of human habitation found in archaeological sites across the region. The Russian conquest of Siberia began in the late 16th century, leading to the incorporation of the region into the Russian Empire.
Major Historical Events
Some of the major historical events that shaped Siberia include:
- The Russian exploration and colonization of Siberia in the 16th and 17th centuries.
- The construction of the Trans-Siberian Railway in the late 19th century.
- The establishment of Siberian exile systems during the Tsarist and Soviet eras.
Siberia's Economy
Siberia's economy is heavily reliant on its natural resources and industrial sectors. The region contributes significantly to Russia's GDP through its exports of oil, natural gas, and metals. In recent years, efforts have been made to diversify the economy by promoting agriculture, tourism, and technology.
Key Economic Sectors
The key economic sectors in Siberia include:
- Energy: Oil and natural gas extraction and processing.
- Mining: Extraction of precious metals and minerals.
- Agriculture: Production of grains, livestock, and dairy products.
Environmental Challenges in Siberia
Siberia faces several environmental challenges, including climate change, deforestation, and pollution. The melting of permafrost in the region poses a significant threat to infrastructure and ecosystems. Efforts are underway to address these challenges through sustainable development practices and international cooperation.
Tourism in Siberia
Siberia offers unique opportunities for adventure tourism, cultural exploration, and eco-tourism. The region's natural beauty and rich cultural heritage attract visitors from around the world. Popular destinations include Lake Baikal, the Sayan Mountains, and the Altai Republic.
Popular Tourist Destinations
Some of the most popular tourist destinations in Siberia include:
- Lake Baikal: The world's deepest freshwater lake, known for its crystal-clear waters and diverse wildlife.
- Sayan Mountains: A scenic mountain range offering hiking and skiing opportunities.
- Altai Republic: A region famous for its stunning landscapes and ancient petroglyphs.
Conclusion
In summary, Siberia is a vast and diverse region located in Northern Asia, forming an integral part of the Russian Federation. Its geographical positioning, rich natural resources, and unique cultural heritage make it a fascinating subject of study and exploration. Understanding where is Siberia located and its significance in global contexts is crucial for anyone interested in geography, economics, and environmental studies.
We invite you to share your thoughts and questions in the comments section below. For more informative articles on global regions and their significance, explore our website further. Together, let's continue to expand our knowledge and appreciation of the world's diverse landscapes and cultures.
Data Source: United Nations, World Bank, Russian Federal State Statistics Service